Salmonellosis (salmonella poisoning) is a leading cause of foodborne illness in the U.S., with over one million illnesses per year. Salmonellosis is transmitted through the consumption of contaminated food products, including raw or under-cooked poultry, eggs, meat, raw or unpasteurized dairy products, and fruits and vegetables. It can also be transferred from handling pets — particularly some birds and reptiles.
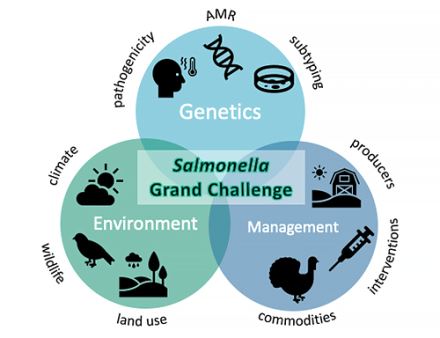
To combat its harmful effects, USDA is launching a "Grand Challenge" initiative to combat Salmonella. Learn how ARS is using the Grand Challenge to determine ways to identify and reduce Salmonella infections by reading our Under the Microscope Q&A.